Which one of the connectors goes ontop? The pink vaccum or the Black one that connects to the Air intake.. We didnt take notice when pulling the Boost Actuator off i figured the Pink one which i assume is the vac goes ontop.. any help would be awesome thanks!
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Boost Actuator question
- Thread starter 04svtlightn
- Start date
are you talking about for a bypass mod? Cause i atempted that and it didnt really work 
Like on the Boost Acutator, it has to ports one facing the firewall and the other facing the front of the trunk. There are 2 connectors, a pink 1 which I assume is the Vaccum and a black one that comes from the Air Intake, which one goes where? does the Pink line go on top or does the black one?
on my stock L the pink line is on the top - but it points to the PS reservior
Start the truck and let it idle, connect the one with vacuum on it (usually pink) to the top of the boost actuator, watch the lever on the actuator, if it moves, you got the correct line, the other one only develops venturi vacuum and goes to the lower connection.
Do you think these things could throw a code? Cause im fighting a losing battle with my EGR Sensors and EGR Valves.. I have replaced everything that has to do with EGR and my light continues to come on.. I have had 4 places scan it and it is the same code every time... Im almost to the point where i say forget it and take the EGR out, but i was hoping to leave everything stock as i could minus things that needed to be fixed.. and this thing has just been a pain every since i got the truck..
Last edited:
what are the codes that keep coming back?Do you think these things could throw a code? Cause im fighting a losing battle with my EGR Sensors and EGR Valves.. I have replaced everything that has to do with EGR and my light continues to come on.. I have had 4 places scan it and it is the same code every time... Im almost to the point where i say forget it and take the EGR out, but i was hoping to leave everything stock as i could minus things that needed to be fixed.. and this thing has just been a pain every since i got the truck..
Its like clogged EGR Valve.. Failed EGR Seloniod.. But, ive replaced everything that the code has gone off for..
codes
2003 PCED OBD
SECTION 5: Pinpoint Tests
Procedure revision date: 06/02/2003
HE: Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Systems
 HE: Introduction
HE: Introduction
HE1 DTC P0405, P1400: DETERMINE PRESENT DPFEGR PID VOLTAGE
Yes No Fault is currently present. Key OFF. GO to HE2 . Fault is intermittent. GO to HE5 .
HE2 INDUCE OPPOSITE D.P.F. EGR SENSOR VOLTAGE
Yes No REPLACE D.P.F. EGR sensor. GO to HE3 .
HE3 CHECK VREF AND SIG RTN CIRCUITS FOR OPEN IN HARNESS TO D.P.F. EGR SENSOR
Yes No Key OFF. GO to HE4 . GO to C1 .
HE4 CHECK DPFEGR CIRCUIT FOR SHORT TO GROUND AND SIG RTN IN HARNESS
Yes No REPLACE PCM (refer to Section 2, Flash Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EEPROM) ). REPAIR short circuit.
HE5 PERFORM WIGGLE TEST ON D.P.F. EGR SENSOR AND CIRCUIT WHILE MONITORING DPFEGR PID FOR A SUDDEN CHANGE
Yes No REPAIR as necessary. Unable to duplicate or identify fault at this time. GO to Z1 .
HE10 DTC P0406, P1401: DETERMINE PRESENT DPFEGR PID VOLTAGE
Yes No Fault is currently present. Key OFF. GO to HE11 . Fault is intermittent. GO to HE19 .
HE11 CHECK DPFEGR CIRCUIT FOR SHORT TO PWR
Yes No Key OFF. GO to HE12 . GO to HE13 .
HE12 CHECK DPFEGR CIRCUIT FOR SHORT TO PWR IN HARNESS
Yes No REPAIR short circuit. REPLACE PCM (refer to Section 2, Flash Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EEPROM) ).
HE13 VERIFY SCAN TOOL COMMUNICATION
Yes No IMMEDIATELY REMOVE jumper wire. GO to HE19 . GO to HE14 .
HE14 INDUCE OPPOSITE D.P.F. EGR SENSOR VOLTAGE
Yes No REMOVE jumper. GO to HE15 . Unable to induce opposite signal. Key OFF. GO to HE17 .
HE15 CHECK VREF VOLTAGE TO D.P.F. EGR SENSOR
Yes No REPLACE D.P.F. EGR sensor. GO to C1 .
HE17 CHECK DPFEGR CIRCUIT FOR OPEN IN HARNESS
Yes No GO to HE18 . REPAIR open circuit.
HE18 CHECK SIG RTN CIRCUIT FOR OPEN IN HARNESS
Yes No REPLACE PCM (refer to Section 2, Flash Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EEPROM) ). REPAIR open circuit.
HE19 CHECK DPFEGR CIRCUIT FOR SHORT TO VREF IN HARNESS
Yes No REPLACE PCM (refer to Section 2, Flash Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EEPROM) ). REPAIR short circuit.
HE20 PERFORM WIGGLE TEST ON D.P.F. EGR SENSOR AND CIRCUIT WHILE MONITORING DPFEGR PID FOR A SUDDEN CHANGE
Yes No REPAIR as necessary. Unable to duplicate or identify fault at this time. GO to Z1 .
HE21 CHECK FOR PRESENCE OF DTC P1405 WITH DTC P0402
Yes No GO to HE50 . GO to HE22 .
HE22 DTC P0402: CHECK FOR EGR FLOW AT IDLE WITH EGR VACUUM HOSE DISCONNECTED
Yes No Key OFF. INSPECT pressure hoses first for pinching and icing. If OK, REMOVE and INSPECT the EGR valve and EGR tube for signs of contamination, unusual wear, carbon deposits, binding and other damage. REPAIR as necessary. RECONNECT vacuum hose to EGR valve. GO to HE23 .
HE23 CHECK FOR EGR FLOW AT IDLE WITH EGR VACUUM HOSE CONNECTED
Yes No Possible EGR flow at idle. GO to HE24 . Fault is intermittent. INSPECT pressure hoses for pinching and icing. REPAIR as necessary. GO to HE31 .
HE24 CHECK EGR SYSTEM VACUUM HOSES FOR INTEGRITY AND CONNECTION
Yes No RECONNECT vacuum hoses. GO to HE25 . REPAIR vacuum hoses as necessary.
HE25 CHECK D.P.F. EGR SENSOR OUTPUT BY APPLYING VACUUM WITH HAND PUMP
Yes No REPLACE D.P.F. EGR sensor. RECONNECT D.P.F. EGR sensor. GO to HE26 .
HE26 CHECK FOR EGR FLOW AT IDLE WITH EGR VACUUM REGULATOR SOLENOID CONNECTOR OFF
Yes No This indicates a fault in the EGR vacuum regulator solenoid. Key OFF. GO to HE27 . Key OFF. GO to HE28 .
HE27 INSPECT EGR VACUUM REGULATOR SOLENOID VENT FOR PLUGGING
Yes No REPAIR EGR vacuum regulator solenoid as necessary. If unable to repair, REPLACE EGR vacuum regulator solenoid. REPLACE EGR vacuum regulator solenoid.
HE28 CHECK EGR VACUUM REGULATOR SOLENOID COIL RESISTANCE
Yes No GO to HE29 . REPLACE EGR vacuum regulator solenoid.
HE29 CHECK EGRVR CIRCUIT FOR SHORT TO GROUND IN HARNESS
Yes No GO to HE30 . REPAIR short circuit.
HE30 CHECK EGRVR CIRCUIT FOR SHORT TO VREF
Yes No REPLACE PCM (refer to Section 2, Flash Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EEPROM) ). REPAIR short circuit.
HE31 CHECK D.P.F. EGR SENSOR OUTPUT BY APPLYING VACUUM WITH HAND PUMP
Yes No REPLACE D.P.F. EGR sensor. RECONNECT D.P.F. EGR sensor. GO to HE32 .
HE32 CHECK D.P.F. EGR SENSOR VOLTAGE WHILE EXERCISING EGR VALVE
Yes No REMOVE and INSPECT the EGR valve for signs of contamination, unusual wear, carbon deposits, binding and other damage. REPAIR as necessary. Key OFF. GO to HE33 .
HE33 MONITOR EGR VALVE VACUUM WHILE WIGGLING EGRVR CIRCUIT
Yes No ISOLATE fault and REPAIR as necessary. RECONNECT vacuum hose. Key OFF. GO to HE34 .
HE34 INSPECT EGR VACUUM REGULATOR SOLENOID AND VACUUM HOSES FOR POTENTIAL PLUGGING
Yes No REPAIR EGR vacuum regulator solenoid or EGR vacuum hose as necessary. Unable to duplicate or identify fault at this time. GO to Z1 .
HE50 DTC P1405: INSPECT UPSTREAM PRESSURE HOSE CONNECTIONS

Yes No REPAIR as necessary. COMPLETE EGR Monitor Repair Verification Drive Cycle (REFER to Section 2, Drive Cycles ). GO to HE51 .
HE51 INSPECT UPSTREAM PRESSURE HOSE FOR PLUGGING
Yes No REPAIR or REPLACE upstream pressure hose as necessary. COMPLETE EGR Monitor Repair Verification Drive Cycle (REFER to Section 2, Drive Cycles ). GO to HE52 .
HE52 CHECK ORIFICE TUBE ASSEMBLY AND D.P.F. EGR SENSOR
Yes No REPAIR or REPLACE D.P.F. EGR sensor or orifice tube assembly as necessary. COMPLETE EGR Monitor Repair Verification Drive Cycle (REFER to Section 2, Drive Cycles ). GO to HE53 .
HE53 CHECK D.P.F. EGR SENSOR OUTPUT BY APPLYING VACUUM WITH HAND PUMP
Yes No REPLACE D.P.F. EGR sensor. COMPLETE an EGR Monitor Repair Verification Drive Cycle (REFER to Section 2, Drive Cycles ). Unable to duplicate or identify fault at this time. GO to Z1 .
HE60 DTC P1406: INSPECT DOWNSTREAM PRESSURE HOSE CONNECTIONS

Yes No REPAIR as necessary. GO to HE61 .
HE61 INSPECT DOWNSTREAM PRESSURE HOSE FOR PLUGGING
Yes No REPAIR or REPLACE as necessary. GO to HE62 .
HE62 CHECK ORIFICE TUBE ASSEMBLY AND D.P.F. EGR SENSOR
Yes No REPAIR or REPLACE D.P.F. EGR sensor or orifice tube assembly as necessary. GO to HE63 .
HE63 CHECK EGR SENSOR OUTPUT BY APPLYING VACUUM WITH HAND PUMP
Yes No REPLACE D.P.F. EGR sensor. Unable to duplicate or identify fault at this time. GO to Z1 .
HE70 DTC P0401: RUN KOER SELF-TEST
Yes No Fault is currently present. GO to HE71 . GO to HE90 .
HE71 DTC P1408: RETRIEVE CONTINUOUS MEMORY DTCS
Yes No GO to HE60 . GO to HE72 .
HE72 RUN KOER SELF-TEST WHILE MONITORING EGR VACUUM
Yes No The vacuum indicated is sufficient to open the EGR valve. Fault is unlikely to be in EGR vacuum control system. Key OFF. GO to HE73 . The vacuum indicated is insufficient to open the EGR valve. Key OFF. GO to HE80 .
HE73 INSPECT D.P.F. EGR SENSOR PRESSURE HOSES

Yes No REPAIR pressure hoses as necessary. GO to HE74 .
HE74 CHECK D.P.F. EGR SENSOR OUTPUT BY APPLYING VACUUM WITH HAND PUMP
Yes No REPLACE D.P.F. EGR sensor. RECONNECT pressure hoses. GO to HE76 .
HE76 CHECK EGR VALVE FUNCTION BY APPLYING VACUUM WITH HAND PUMP
Yes No GO to HE82 . REMOVE and INSPECT the EGR valve for signs of contamination, unusual wear, carbon deposits, binding, leaking diaphragm and other damage. If EGR valve is OK, look for an obstructed EGR port in the intake manifold or plugged orifice tube assembly. REPAIR as necessary.
HE80 PHYSICALLY INSPECT ALL VACUUM LINES BETWEEN EGR VALVE, EVR AND VACUUM SOURCE
Yes No REPAIR as necessary. Key OFF. GO to HE81 .
HE81 CHECK ENGINE VACUUM
Yes No Key OFF. GO to HE82 . ISOLATE possible base engine concern and REPAIR as necessary.
HE82 CHECK VPWR VOLTAGE TO EGR VACUUM REGULATOR SOLENOID
Yes No Key OFF. GO to HE83 . REPAIR open circuit.
HE83 CHECK EGR VACUUM REGULATOR SOLENOID RESISTANCE
Yes No GO to HE84 . REPLACE EGR vacuum regulator solenoid.
HE84 CHECK EGRVR CIRCUIT FOR SHORT TO PWR IN HARNESS
Yes No REPAIR short circuit. Key OFF. GO to HE85 .
HE85 CHECK EGRVR CIRCUIT FOR OPEN IN HARNESS
Yes No RECONNECT PCM and EGR vacuum regulator solenoid. GO to HE86 . REPAIR open in EGRVR circuit.
HE86 CHECK EGR VACUUM REGULATOR SOLENOID VACUUM OUTPUT CAPABILITY BY GROUNDING EGRVR CIRCUIT
Yes No REPLACE PCM (refer to section 2, Flash Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EEPROM) ). REPLACE EGR vacuum regulator solenoid.
HE90 INSPECT EGR SYSTEM FOR AN INTERMITTENT FAILURE
Yes No REPAIR fault as necessary. GO to HE91 .
HE91 INSPECT D.P.F. EGR SENSOR PRESSURE HOSES

Yes No REPAIR pressure hoses as necessary. GO to HE92 .
HE92 CHECK D.P.F. EGR SENSOR OUTPUT BY APPLYING VACUUM WITH HAND PUMP
Yes No REPLACE D.P.F. EGR sensor. RECONNECT pressure hoses. GO to HE93 .
HE93 CHECK EGR VALVE FUNCTION BY APPLYING VACUUM WITH HAND PUMP
Yes No GO to HE94 . REMOVE and INSPECT the EGR valve for signs of contamination, unusual wear, carbon deposits, binding, leaking diaphragm and other damage. If EGR valve is OK, look for an obstructed EGR port in the intake manifold. REPAIR as necessary.
HE94 INSPECT EGR VACUUM SIGNAL SUPPLY FOR INTERMITTENT FAILURE
Yes No ISOLATE fault and REPAIR as necessary. Unable to duplicate or identify fault at this time. (In cold climates, the EGR valve may temporarily freeze shut and thaw when the engine warms up causing the intermittent DTC.) GO to Z1 .
HE100 EGR DIAGNOSIS BY SYMPTOM: CHECK FOR EGR FLOW WITH EGR VACUUM HOSE DISCONNECTED AND PLUGGED
Yes No The DPFEGR PID voltage is indicating EGR flow at idle. Since the EGR vacuum hose is disconnected and plugged, the fault is most likely in the EGR valve. REMOVE and INSPECT the EGR valve for signs of contamination, unusual wear, carbon deposits, binding and other damage. REPAIR as necessary. This indicates a fault in the EGR valve vacuum supply. INSPECT the EGR vacuum regulator solenoid vent and vent filter for restrictions. REPAIR as necessary. If OK, REPLACE EGR vacuum regulator solenoid.
HE110 DTC P0403, P1409: CHECK EGR VACUUM REGULATOR SOLENOID RESISTANCE
Yes No GO to HE111 . REPLACE EGR vacuum regulator solenoid.
HE111 CHECK VPWR VOLTAGE TO EGR VACUUM REGULATOR SOLENOID
Yes No Key OFF. GO to HE112 . REPAIR open in VPWR circuit.
HE112 CHECK EGRVR CIRCUIT FOR OPEN IN HARNESS
Yes No GO to HE113 . REPAIR open in EGRVR circuit.
HE113 CHECK EGRVR CIRCUIT FOR SHORT TO POWER IN HARNESS
Yes No Key OFF. GO to HE114 . REPAIR short circuit.
HE114 CHECK EGRVR CIRCUIT FOR SHORT TO GROUND IN HARNESS
Yes No REPLACE PCM (refer to Section 2, Flash Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EEPROM) ). REPAIR short circuit.
HE120 CONTINUOUS MEMORY DTC P0403, P1409: WIGGLE EGR VACUUM REGULATOR SOLENOID WHILE MONITORING VPWR
Yes No ISOLATE fault and REPAIR as necessary. Unable to duplicate or identify fault at this time. GO to Z1 .
Its like clogged EGR Valve.. Failed EGR Seloniod.. But, ive replaced everything that the code has gone off for..
2003 PCED OBD
SECTION 5: Pinpoint Tests
Procedure revision date: 06/02/2003
HE: Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Systems

HE1 DTC P0405, P1400: DETERMINE PRESENT DPFEGR PID VOLTAGE
- Key ON, Engine OFF.
- Access DPFEGR PID.
Yes No Fault is currently present. Key OFF. GO to HE2 . Fault is intermittent. GO to HE5 .
HE2 INDUCE OPPOSITE D.P.F. EGR SENSOR VOLTAGE
- Disconnect D.P.F. EGR sensor.
- Key ON, Engine OFF.
Yes No REPLACE D.P.F. EGR sensor. GO to HE3 .
HE3 CHECK VREF AND SIG RTN CIRCUITS FOR OPEN IN HARNESS TO D.P.F. EGR SENSOR
- Measure voltage between VREF and SIG RTN circuits at the D.P.F. EGR sensor harness connector.
Yes No Key OFF. GO to HE4 . GO to C1 .
HE4 CHECK DPFEGR CIRCUIT FOR SHORT TO GROUND AND SIG RTN IN HARNESS
- Note: Refer to the PCM connector pin numbers in the beginning of this pinpoint test.
- Disconnect scan tool.
- Disconnect PCM.
- Measure resistance between DPFEGR and SIG. RTN circuits at the PCM harness connector.
- Measure resistance between DPFEGR circuit at the PCM harness connector and battery (-) terminal.
Yes No REPLACE PCM (refer to Section 2, Flash Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EEPROM) ). REPAIR short circuit.
HE5 PERFORM WIGGLE TEST ON D.P.F. EGR SENSOR AND CIRCUIT WHILE MONITORING DPFEGR PID FOR A SUDDEN CHANGE
- While monitoring DPFEGR PID, tap on the D.P.F. EGR sensor and wiggle the wiring while looking for a sudden change in value as an indication of an intermittent.
Yes No REPAIR as necessary. Unable to duplicate or identify fault at this time. GO to Z1 .
HE10 DTC P0406, P1401: DETERMINE PRESENT DPFEGR PID VOLTAGE
- Key ON, Engine OFF.
- Access DPFEGR PID.
Yes No Fault is currently present. Key OFF. GO to HE11 . Fault is intermittent. GO to HE19 .
HE11 CHECK DPFEGR CIRCUIT FOR SHORT TO PWR
- Disconnect D.P.F. EGR sensor.
- Key ON, Engine OFF.
- Measure voltage between DPFEGR circuit at the D.P.F. EGR sensor harness connector and battery (-) terminal.
Yes No Key OFF. GO to HE12 . GO to HE13 .
HE12 CHECK DPFEGR CIRCUIT FOR SHORT TO PWR IN HARNESS
- Note: Refer to the PCM connector pin numbers in the beginning of this pinpoint test.
- Disconnect PCM.
- Key ON, Engine OFF.
- Measure voltage between DPFEGR circuit at the PCM harness connector and battery (-) terminal.
Yes No REPAIR short circuit. REPLACE PCM (refer to Section 2, Flash Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EEPROM) ).
HE13 VERIFY SCAN TOOL COMMUNICATION
- Connect jumper wire between DPFEGR and SIG RTN circuits at the D.P.F. EGR sensor harness connector.
- Access DPFEGR PID.
Yes No IMMEDIATELY REMOVE jumper wire. GO to HE19 . GO to HE14 .
HE14 INDUCE OPPOSITE D.P.F. EGR SENSOR VOLTAGE
- Key OFF.
- Disconnect jumper wire between DPFEGR and SIG RTN circuits at the D.P.F. EGR sensor harness connector.
- Connect jumper wire between DPFEGR and VREF circuits at the D.P.F. EGR sensor harness connector.
- Key ON, Engine OFF.
- Access DPFEGR PID.
Yes No REMOVE jumper. GO to HE15 . Unable to induce opposite signal. Key OFF. GO to HE17 .
HE15 CHECK VREF VOLTAGE TO D.P.F. EGR SENSOR
- Measure voltage between VREF and SIG RTN circuits at the D.P.F. EGR sensor harness connector.
Yes No REPLACE D.P.F. EGR sensor. GO to C1 .
HE17 CHECK DPFEGR CIRCUIT FOR OPEN IN HARNESS
- Disconnect PCM.
- Measure resistance of DPFEGR circuit between PCM harness connector pin and D.P.F. EGR sensor harness connector.
Yes No GO to HE18 . REPAIR open circuit.
HE18 CHECK SIG RTN CIRCUIT FOR OPEN IN HARNESS
- Measure resistance of SIG RTN circuit between PCM harness connector pin and D.P.F. EGR sensor harness connector.
Yes No REPLACE PCM (refer to Section 2, Flash Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EEPROM) ). REPAIR open circuit.
HE19 CHECK DPFEGR CIRCUIT FOR SHORT TO VREF IN HARNESS
- Disconnect PCM.
- Measure resistance between DPFEGR circuit and VREF circuit(s) at the PCM harness connector.
Yes No REPLACE PCM (refer to Section 2, Flash Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EEPROM) ). REPAIR short circuit.
HE20 PERFORM WIGGLE TEST ON D.P.F. EGR SENSOR AND CIRCUIT WHILE MONITORING DPFEGR PID FOR A SUDDEN CHANGE
- While monitoring DPFEGR PID, tap on the D.P.F. EGR sensor and wiggle the harness while looking for a sudden change in value as an indication of an intermittent.
Yes No REPAIR as necessary. Unable to duplicate or identify fault at this time. GO to Z1 .
HE21 CHECK FOR PRESENCE OF DTC P1405 WITH DTC P0402
Yes No GO to HE50 . GO to HE22 .
HE22 DTC P0402: CHECK FOR EGR FLOW AT IDLE WITH EGR VACUUM HOSE DISCONNECTED
- Disconnect vacuum hose at EGR valve and plug hose.
- Run Key On Engine Running (KOER) Self-Test.
Yes No Key OFF. INSPECT pressure hoses first for pinching and icing. If OK, REMOVE and INSPECT the EGR valve and EGR tube for signs of contamination, unusual wear, carbon deposits, binding and other damage. REPAIR as necessary. RECONNECT vacuum hose to EGR valve. GO to HE23 .
HE23 CHECK FOR EGR FLOW AT IDLE WITH EGR VACUUM HOSE CONNECTED
- EGR vacuum hose connected.
- Run KOER Self-Test.
Yes No Possible EGR flow at idle. GO to HE24 . Fault is intermittent. INSPECT pressure hoses for pinching and icing. REPAIR as necessary. GO to HE31 .
HE24 CHECK EGR SYSTEM VACUUM HOSES FOR INTEGRITY AND CONNECTION
- Note: A pinched or plugged EGR vacuum hose can trap vacuum between the EGR vacuum regulator solenoid and EGR valve, not allowing the EGR valve to close.
- Trace each vacuum hose from EGR vacuum regulator solenoid and verify that each hose is connected correctly (refer to vehicle vacuum diagram label).
- Verify that the EGR valve vacuum hose is not pinched or plugged and is routed properly.
Yes No RECONNECT vacuum hoses. GO to HE25 . REPAIR vacuum hoses as necessary.
HE25 CHECK D.P.F. EGR SENSOR OUTPUT BY APPLYING VACUUM WITH HAND PUMP
- Disconnect pressure hoses at D.P.F. EGR sensor.
- Connect a hand vacuum pump to the downstream connection at sensor (intake manifold side of sensor or the smaller diameter pickup tube).
- Key ON, Engine OFF.
- Access DPFEGR PID and note PID value.
- Apply 27 to 30 kPa (8 to 9 in-Hg) vacuum to the D.P.F. EGR sensor and hold for 5 seconds.
- Quickly release vacuum.
- The DPFEGR PID voltage must be between 0.2V and 1.3V DC with the key ON and no vacuum applied.
- The DPFEGR PID voltage must increase to greater than 4.0V DC with the vacuum applied.
- The DPFEGR PID must drop to less than 1.5V DC in less than 3 seconds when vacuum is released.
Yes No REPLACE D.P.F. EGR sensor. RECONNECT D.P.F. EGR sensor. GO to HE26 .
HE26 CHECK FOR EGR FLOW AT IDLE WITH EGR VACUUM REGULATOR SOLENOID CONNECTOR OFF
- Disconnect vacuum hose at EGR valve and connect hose to vacuum gauge.
- Start engine.
- While monitoring vacuum gauge, disconnect the EGR vacuum regulator solenoid harness connector.
- The EGR valve requires vacuum greater than 5.4 kPa (1.6 in-Hg) to begin to open. If the vacuum reading remains greater than 5.4 kPa (1.6 in-Hg) after the EGR vacuum regulator solenoid is electrically disconnected, this would indicate a mechanical fault in the EGR vacuum regulator solenoid.
Yes No This indicates a fault in the EGR vacuum regulator solenoid. Key OFF. GO to HE27 . Key OFF. GO to HE28 .
HE27 INSPECT EGR VACUUM REGULATOR SOLENOID VENT FOR PLUGGING
- Note: A plugged EGR vacuum regulator solenoid vent will not allow EGR vacuum to vent to atmosphere.
- Disconnect EGR vacuum regulator solenoid vacuum hoses.
- Remove EGR vacuum regulator solenoid vent cap (if removable).
- Remove filter and inspect for blockage or icing in some cases.
- With the EGR vacuum supply port plugged, apply 34 to 51 kPa (10 to 15 in-Hg) of vacuum directly to EGR vacuum regulator solenoid vacuum source port with a hand vacuum pump. If the vacuum holds or is slow to release to atmosphere, the EGR vacuum regulator solenoid vent could be plugged or restricted.

Yes No REPAIR EGR vacuum regulator solenoid as necessary. If unable to repair, REPLACE EGR vacuum regulator solenoid. REPLACE EGR vacuum regulator solenoid.
HE28 CHECK EGR VACUUM REGULATOR SOLENOID COIL RESISTANCE
- Measure resistance across EGR vacuum regulator solenoid.
Yes No GO to HE29 . REPLACE EGR vacuum regulator solenoid.
HE29 CHECK EGRVR CIRCUIT FOR SHORT TO GROUND IN HARNESS
- Note: Refer to the PCM connector pin numbers in the beginning of this pinpoint test.
- Disconnect scan tool from DLC.
- Disconnect PCM.
- Measure resistance between EGRVR circuit at the PCM harness connector and battery (-) terminal.
Yes No GO to HE30 . REPAIR short circuit.
HE30 CHECK EGRVR CIRCUIT FOR SHORT TO VREF
- Measure resistance between EGRVR circuit and VREF circuit(s) at the PCM harness connector.
Yes No REPLACE PCM (refer to Section 2, Flash Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EEPROM) ). REPAIR short circuit.
HE31 CHECK D.P.F. EGR SENSOR OUTPUT BY APPLYING VACUUM WITH HAND PUMP
- Disconnect pressure hoses at D.P.F. EGR sensor.
- Connect a hand vacuum pump to the downstream connection at sensor (intake manifold side of sensor or the smaller diameter pickup tube).
- Key ON, Engine OFF.
- Access DPFEGR PID and note PID value.
- Apply 27 to 30 kPa (8 to 9 in-Hg) vacuum to the D.P.F. EGR sensor and hold for 5 seconds.
- Quickly release vacuum.
- The DPFEGR PID voltage must be between 0.2V and 1.3V DC with the key ON and no vacuum applied.
- The DPFEGR PID voltage must increase to greater than 4.0V DC with the vacuum applied.
- The DPFEGR PID must drop to less than 1.5V DC in less than 3 seconds when vacuum is released.
Yes No REPLACE D.P.F. EGR sensor. RECONNECT D.P.F. EGR sensor. GO to HE32 .
HE32 CHECK D.P.F. EGR SENSOR VOLTAGE WHILE EXERCISING EGR VALVE
- Key ON, Engine OFF.
- View DPFEGR PID and make note of voltage.
- Typical D.P.F. EGR sensor voltage with no EGR flow is between 0.2V and 1.3V DC.
- Disconnect vacuum hose at EGR valve and plug hose.
- Connect a hand vacuum pump to EGR valve.
- Start engine.
- Observe DPFEGR PID at idle and compare to the key ON engine OFF voltage. (A higher voltage at idle may be due to a non-seating EGR valve.)
- Apply just enough vacuum to EGR valve to open it 7-10 kPa (2-3 in-Hg) without stalling engine and release vacuum. Repeat several times while observing DPFEGR PID. (DPFEGR PID voltage must increase as valve begins to open and return to initial value as vacuum is released. A slow to return voltage could be an indication of a binding or a slow-closing EGR valve.)
Yes No REMOVE and INSPECT the EGR valve for signs of contamination, unusual wear, carbon deposits, binding and other damage. REPAIR as necessary. Key OFF. GO to HE33 .
HE33 MONITOR EGR VALVE VACUUM WHILE WIGGLING EGRVR CIRCUIT
- Note: An intermittent short to GND in the EGRVR circuit will cause the vacuum applied to the EGR valve to be higher than normal while the short is present. The vacuum available at the EGR valve at idle is normally below 3.4 kPa (1.0 in-Hg) and it takes about 5.4 kPa (1.6 in-Hg) for the valve to begin to open.
- Remove hand vacuum pump.
- Connect vacuum gauge to EGR valve vacuum hose.
- Key ON, Engine RUNNING.
- Observe vacuum gauge for an indication of a fault while performing the following:
- Lightly tap on the EGR vacuum regulator solenoid; wiggle the EGR vacuum regulator solenoid connector and vehicle harness between solenoid and PCM. A fault is indicated by a sudden jump in vacuum reading.
Yes No ISOLATE fault and REPAIR as necessary. RECONNECT vacuum hose. Key OFF. GO to HE34 .
HE34 INSPECT EGR VACUUM REGULATOR SOLENOID AND VACUUM HOSES FOR POTENTIAL PLUGGING
- Remove EGR vacuum regulator solenoid vent filter and inspect for contamination and excessive water absorption. (In cold climate, excessive water in filter could freeze and plug the EGR vacuum regulator solenoid vent.)
- Inspect EGR vacuum hose for possible blockage or pinching.
Yes No REPAIR EGR vacuum regulator solenoid or EGR vacuum hose as necessary. Unable to duplicate or identify fault at this time. GO to Z1 .
HE50 DTC P1405: INSPECT UPSTREAM PRESSURE HOSE CONNECTIONS
- Inspect upstream hose at D.P.F. EGR sensor and orifice tube assembly for disconnect or poor connection.

Yes No REPAIR as necessary. COMPLETE EGR Monitor Repair Verification Drive Cycle (REFER to Section 2, Drive Cycles ). GO to HE51 .
HE51 INSPECT UPSTREAM PRESSURE HOSE FOR PLUGGING
- Note: It is essential that ONLY the correct Ford service D.P.F. EGR sensor pressure hose be used.
- Visually inspect upstream pressure hose routing. Hose must not be pinched or have dips in it where water could settle or freeze.
- Remove upstream pressure hose and carefully inspect for plugging, water or leaks.
Yes No REPAIR or REPLACE upstream pressure hose as necessary. COMPLETE EGR Monitor Repair Verification Drive Cycle (REFER to Section 2, Drive Cycles ). GO to HE52 .
HE52 CHECK ORIFICE TUBE ASSEMBLY AND D.P.F. EGR SENSOR
- Inspect the upstream connection on the D.P.F. EGR sensor for plugging or damage at the sensor.
- Inspect the exhaust manifold side pressure pickup tube at the orifice tube assembly for plugging or damage.
Yes No REPAIR or REPLACE D.P.F. EGR sensor or orifice tube assembly as necessary. COMPLETE EGR Monitor Repair Verification Drive Cycle (REFER to Section 2, Drive Cycles ). GO to HE53 .
HE53 CHECK D.P.F. EGR SENSOR OUTPUT BY APPLYING VACUUM WITH HAND PUMP
- Disconnect pressure hoses at D.P.F. EGR sensor.
- Connect a hand vacuum pump to the downstream connection at sensor (intake manifold side of sensor or the smaller diameter pickup tube).
- Key ON, Engine OFF.
- Access DPFEGR PID and note PID value.
- Apply 27 to 30 kPa (8 to 9 in-Hg) vacuum to the D.P.F. EGR sensor and hold for a few seconds.
- Quickly release vacuum.
- The DPFEGR PID voltage must be between 0.2V and 1.3V DC with the key ON and no vacuum applied.
- The DPFEGR PID voltage must increase to greater than 4.0V DC with the vacuum applied.
- The DPFEGR PID must drop to less than 1.5V DC in less than 3 seconds when vacuum is released.
Yes No REPLACE D.P.F. EGR sensor. COMPLETE an EGR Monitor Repair Verification Drive Cycle (REFER to Section 2, Drive Cycles ). Unable to duplicate or identify fault at this time. GO to Z1 .
HE60 DTC P1406: INSPECT DOWNSTREAM PRESSURE HOSE CONNECTIONS
- Note: If the fault is currently present, DTC P1408 will appear when running Key On Engine Running (KOER) Self-Test.
Verify EGR valve is securely attached and exhaust gasses are not leaking from the sealing surface. - Inspect downstream hose at D.P.F. EGR sensor and orifice tube assembly for disconnect or poor connection.

Yes No REPAIR as necessary. GO to HE61 .
HE61 INSPECT DOWNSTREAM PRESSURE HOSE FOR PLUGGING
- Note: It is essential that ONLY the correct Ford service D.P.F. EGR sensor pressure hose be used.
- Visually inspect downstream pressure hose routing. Hose must not be pinched or have dips in it where water can settle or freeze.
- Remove downstream pressure hose and carefully inspect for plugging, water or leaks.
Yes No REPAIR or REPLACE as necessary. GO to HE62 .
HE62 CHECK ORIFICE TUBE ASSEMBLY AND D.P.F. EGR SENSOR
- Inspect the connections at the D.P.F. EGR sensor for plugging or damage.
- Inspect the intake manifold side pressure pickup tube and orifice tube assembly for plugging, loose connection or damage.
Yes No REPAIR or REPLACE D.P.F. EGR sensor or orifice tube assembly as necessary. GO to HE63 .
HE63 CHECK EGR SENSOR OUTPUT BY APPLYING VACUUM WITH HAND PUMP
- Disconnect pressure hoses at D.P.F. EGR sensor.
- Connect a hand vacuum pump to the downstream connection at sensor (intake manifold side of sensor or the smaller diameter pickup tube).
- Key ON, Engine OFF.
- Access DPFEGR PID and note PID value.
- Apply 27 to 30 kPa (8 to 9 in-Hg) vacuum to the D.P.F. EGR sensor and hold for 5 seconds.
- Quickly release vacuum.
- The DPFEGR PID voltage must be between 0.2V and 1.3V DC with the key ON and no vacuum applied.
- The DPFEGR PID voltage must increase to greater than 4.0V DC with the vacuum applied.
- The DPFEGR PID must drop to less than 1.5V DC in less than 3 seconds when vacuum is released.
Yes No REPLACE D.P.F. EGR sensor. Unable to duplicate or identify fault at this time. GO to Z1 .
HE70 DTC P0401: RUN KOER SELF-TEST
- Run KOER Self-Test.
Yes No Fault is currently present. GO to HE71 . GO to HE90 .
HE71 DTC P1408: RETRIEVE CONTINUOUS MEMORY DTCS
- Note: If any DTC other than DTC P1406 appears, note the DTC and refer to Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Charts in Section 4 after completing this Pinpoint Test.
- Retrieve all Continuous Memory DTCs.
Yes No GO to HE60 . GO to HE72 .
HE72 RUN KOER SELF-TEST WHILE MONITORING EGR VACUUM
- Disconnect vacuum hose at EGR valve and connect hose to a vacuum gauge. Note: Since the EGR vacuum hose is disconnected, ignore DTCs during this KOER Self-Test.
- Run Key On Engine Running (KOER) Self-Test while monitoring gauge. Approximately 30 seconds into test, EGR flow will be requested for a few seconds. The vacuum at this time should increase above 5.4 kPa (1.6 in-Hg) to open the valve.
Yes No The vacuum indicated is sufficient to open the EGR valve. Fault is unlikely to be in EGR vacuum control system. Key OFF. GO to HE73 . The vacuum indicated is insufficient to open the EGR valve. Key OFF. GO to HE80 .
HE73 INSPECT D.P.F. EGR SENSOR PRESSURE HOSES
- Visually inspect both pressure hoses for reversed connection at D.P.F. EGR sensor or at orifice tube assembly.
- Inspect both hoses for improper routing. Hoses should not be pinched or have dips where water could settle or freeze.
- Inspect both hoses for leaks and blockage.
- Inspect D.P.F. EGR sensor and orifice tube assembly for blockage or damage at the pickup tubes.

Yes No REPAIR pressure hoses as necessary. GO to HE74 .
HE74 CHECK D.P.F. EGR SENSOR OUTPUT BY APPLYING VACUUM WITH HAND PUMP
- Disconnect pressure hoses at D.P.F. EGR sensor.
- Connect a hand vacuum pump to the downstream connection at sensor (intake manifold side of sensor or the smaller diameter pickup tube.)
- Key ON, Engine OFF.
- Access DPFEGR PID and note PID value.
- Apply 27-30 kPa (8-9 in-Hg) vacuum to the D.P.F. EGR sensor and hold for 5 seconds.
- Quickly release vacuum.
- The DPFEGR PID voltage must be between 0.2V and 1.3V DC with the key ON and no vacuum applied.
- The DPFEGR PID voltage must increase to greater than 4.0V DC with the vacuum applied.
- The DPFEGR PID must drop to less than 1.5V DC in less than 3 seconds when vacuum is released.
Yes No REPLACE D.P.F. EGR sensor. RECONNECT pressure hoses. GO to HE76 .
HE76 CHECK EGR VALVE FUNCTION BY APPLYING VACUUM WITH HAND PUMP
- Disconnect vacuum hose at EGR valve and plug hose.
- Connect a hand vacuum pump to EGR valve.
- Start engine.
- Access DPFEGR and RPM PIDs.
- Slowly apply 27 to 34 kPa (8 to 10 in-Hg) of vacuum to the EGR valve and hold it for 10 seconds. If engine wants to stall, increase rpm with throttle to maintain a minimum of 1000 RPM.
- Look for the following:
- EGR valve starts opening at about 5.4 kPa (1.6 in-Hg) vacuum indicated by increasing DPFEGR PID voltage.
- DPFEGR PID voltage increasing until EGR valve is fully open. DPFEGR PID must read 2.5V DC minimum with full vacuum applied.
- DPFEGR PID voltage steady when vacuum is held. If voltage drops within a few seconds, the EGR valve or vacuum source can be leaking.
Yes No GO to HE82 . REMOVE and INSPECT the EGR valve for signs of contamination, unusual wear, carbon deposits, binding, leaking diaphragm and other damage. If EGR valve is OK, look for an obstructed EGR port in the intake manifold or plugged orifice tube assembly. REPAIR as necessary.
HE80 PHYSICALLY INSPECT ALL VACUUM LINES BETWEEN EGR VALVE, EVR AND VACUUM SOURCE
- Inspect all vacuum lines for leaks, kinks, pinches, disconnects, blockage, misrouting or any physical damage.
Yes No REPAIR as necessary. Key OFF. GO to HE81 .
HE81 CHECK ENGINE VACUUM
- Disconnect EVR vacuum hose at vacuum source.
- Connect vacuum gauge to vacuum source.
- Start engine.
- With engine warm and at idle, monitor vacuum gauge.
Yes No Key OFF. GO to HE82 . ISOLATE possible base engine concern and REPAIR as necessary.
HE82 CHECK VPWR VOLTAGE TO EGR VACUUM REGULATOR SOLENOID
- Disconnect EGR vacuum regulator solenoid.
- Key ON, Engine OFF.
- Measure VPWR circuit voltage at EGR vacuum regulator solenoid harness connector.
Yes No Key OFF. GO to HE83 . REPAIR open circuit.
HE83 CHECK EGR VACUUM REGULATOR SOLENOID RESISTANCE
- Measure EGR vacuum regulator solenoid resistance.
Yes No GO to HE84 . REPLACE EGR vacuum regulator solenoid.
HE84 CHECK EGRVR CIRCUIT FOR SHORT TO PWR IN HARNESS
- Note: Refer to the PCM connector pin numbers in the beginning of this pinpoint test.
- Disconnect PCM.
- Key ON, Engine OFF.
- Measure voltage between EGRVR circuit at the PCM harness connector and battery (-) terminal.
Yes No REPAIR short circuit. Key OFF. GO to HE85 .
HE85 CHECK EGRVR CIRCUIT FOR OPEN IN HARNESS
- Measure resistance of EGRVR circuit between PCM harness connector pin and EGR vacuum regulator solenoid harness connector.
Yes No RECONNECT PCM and EGR vacuum regulator solenoid. GO to HE86 . REPAIR open in EGRVR circuit.
HE86 CHECK EGR VACUUM REGULATOR SOLENOID VACUUM OUTPUT CAPABILITY BY GROUNDING EGRVR CIRCUIT
- Disconnect vacuum hose at the EGR valve and connect to a vacuum gauge.
- Key ON, Engine RUNNING.
- With engine at idle, jumper PCM EGRVR circuit to chassis ground. If the EGRVR does not react within 2 seconds, an EGRVR fault may be present.
Yes No REPLACE PCM (refer to section 2, Flash Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EEPROM) ). REPLACE EGR vacuum regulator solenoid.
HE90 INSPECT EGR SYSTEM FOR AN INTERMITTENT FAILURE
- Visually inspect the EGR system for signs of intermittent failure.
Yes No REPAIR fault as necessary. GO to HE91 .
HE91 INSPECT D.P.F. EGR SENSOR PRESSURE HOSES
- Visually inspect both pressure hoses for reversed connection at D.P.F. EGR sensor or at orifice tube assembly.
- Inspect both hoses for improper routing. Hoses should not be pinched or have dips where water could settle or freeze.
- Inspect both hoses for leaks and blockage.
- Inspect D.P.F. EGR sensor and orifice tube assembly for blockage or damage at the pickup tubes.

Yes No REPAIR pressure hoses as necessary. GO to HE92 .
HE92 CHECK D.P.F. EGR SENSOR OUTPUT BY APPLYING VACUUM WITH HAND PUMP
- Disconnect pressure hoses at D.P.F. EGR sensor.
- Connect a hand vacuum pump to the downstream connection at sensor (intake manifold side of sensor or the smaller diameter pickup tube.)
- Key ON, Engine OFF.
- Access DPFEGR PID and note PID value.
- Apply 27-30 kPa (8-9 in-Hg) vacuum to the D.P.F. EGR sensor and hold for 5 seconds.
- Quickly release vacuum.
- The DPFEGR PID voltage must be between 0.2V and 1.3V DC with the key ON and no vacuum applied.
- The DPFEGR PID voltage must increase to greater than 4.0V DC with the vacuum applied.
- The DPFEGR PID must drop to less than 1.5V DC in less than 3 seconds when vacuum is released.
Yes No REPLACE D.P.F. EGR sensor. RECONNECT pressure hoses. GO to HE93 .
HE93 CHECK EGR VALVE FUNCTION BY APPLYING VACUUM WITH HAND PUMP
- Disconnect vacuum hose at EGR valve and plug hose.
- Connect a hand vacuum pump to EGR valve.
- Start engine.
- Access DPFEGR and RPM PIDs.
- Slowly apply 17 to 34 kPa (5 to 10 in-Hg) of vacuum to the EGR valve and hold it for 10 seconds. If engine wants to stall, increase rpm with throttle to maintain a minimum of 800 RPM.
- Look for the following:
- EGR valve starts opening at about 5.4 kPa (1.6 in-Hg) vacuum indicated by increasing DPFEGR PID voltage.
- DPFEGR PID voltage increasing until EGR valve is fully open. DPFEGR PID should read 2.5V DC minimum with full vacuum applied.
- DPFEGR PID voltage steady when vacuum is held. If voltage drops within 5 seconds, the EGR valve or vacuum source could be leaking.
Yes No GO to HE94 . REMOVE and INSPECT the EGR valve for signs of contamination, unusual wear, carbon deposits, binding, leaking diaphragm and other damage. If EGR valve is OK, look for an obstructed EGR port in the intake manifold. REPAIR as necessary.
HE94 INSPECT EGR VACUUM SIGNAL SUPPLY FOR INTERMITTENT FAILURE
- Disconnect plugged hose at EGR valve and connect to a vacuum gauge.
- Key ON, Engine RUNNING.
- Connect a jumper wire between EGRVR circuit and ground to activate the solenoid to full ON. At idle, the vacuum gauge should read above 13.5 kPa (4.0 in-Hg).
- Observe vacuum gauge for an indication of a fault while performing the following:
- Lightly tap on the EGR vacuum regulator solenoid and wiggle the EGR vacuum regulator solenoid connector, vacuum lines and vehicle harness between the solenoid and PCM. A fault is indicated by a sudden drop in vacuum reading.
Yes No ISOLATE fault and REPAIR as necessary. Unable to duplicate or identify fault at this time. (In cold climates, the EGR valve may temporarily freeze shut and thaw when the engine warms up causing the intermittent DTC.) GO to Z1 .
HE100 EGR DIAGNOSIS BY SYMPTOM: CHECK FOR EGR FLOW WITH EGR VACUUM HOSE DISCONNECTED AND PLUGGED
- Note: Perform KOER Self-Test and repair any DTCs before proceeding with this test.
The symptom charts indicate possible EGR flow at idle with no EGR diagnostic trouble codes present.
Possible causes:- EGR valve not fully seating.
- EGR vacuum regulator solenoid vent restricted.
- Damaged EGR vacuum regulator solenoid.
- Disconnect vacuum hose at EGR valve and plug hose.
- Key ON, Engine OFF.
- Access DPFEGR PID and note voltage.
- Start engine.
- With engine at idle, look at the DPFEGR PID voltage and compare to the engine OFF reading. An increase in the voltage at idle indicates that the differential pressure feedback EGR sensor is sensing EGR flow.
Yes No The DPFEGR PID voltage is indicating EGR flow at idle. Since the EGR vacuum hose is disconnected and plugged, the fault is most likely in the EGR valve. REMOVE and INSPECT the EGR valve for signs of contamination, unusual wear, carbon deposits, binding and other damage. REPAIR as necessary. This indicates a fault in the EGR valve vacuum supply. INSPECT the EGR vacuum regulator solenoid vent and vent filter for restrictions. REPAIR as necessary. If OK, REPLACE EGR vacuum regulator solenoid.
HE110 DTC P0403, P1409: CHECK EGR VACUUM REGULATOR SOLENOID RESISTANCE
- Disconnect EGR vacuum regulator solenoid.
- Measure EGR vacuum regulator solenoid resistance.
Yes No GO to HE111 . REPLACE EGR vacuum regulator solenoid.
HE111 CHECK VPWR VOLTAGE TO EGR VACUUM REGULATOR SOLENOID
- Key ON, Engine OFF.
- Measure VPWR circuit voltage at EGR vacuum regulator solenoid harness connector.
Yes No Key OFF. GO to HE112 . REPAIR open in VPWR circuit.
HE112 CHECK EGRVR CIRCUIT FOR OPEN IN HARNESS
- Note: Refer to the PCM connector pin numbers in the beginning of this pinpoint test.
- Disconnect PCM.
- Measure resistance of EGRVR circuit between PCM Pin and EGR vacuum regulator solenoid harness connector.
Yes No GO to HE113 . REPAIR open in EGRVR circuit.
HE113 CHECK EGRVR CIRCUIT FOR SHORT TO POWER IN HARNESS
- Key ON, Engine OFF.
- Measure voltage between EGRVR at the PCM harness connector and battery (-) terminal.
Yes No Key OFF. GO to HE114 . REPAIR short circuit.
HE114 CHECK EGRVR CIRCUIT FOR SHORT TO GROUND IN HARNESS
- Measure resistance between EGRVR and PWR GND circuits at the PCM harness connector.
Yes No REPLACE PCM (refer to Section 2, Flash Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EEPROM) ). REPAIR short circuit.
HE120 CONTINUOUS MEMORY DTC P0403, P1409: WIGGLE EGR VACUUM REGULATOR SOLENOID WHILE MONITORING VPWR
- Note: Refer to the PCM connector pin numbers in the beginning of this pinpoint test.
Note: If DTC P1409 appeared after running Key On Engine Off (KOEO) or Key On Engine Running (KOER) Self-Test, GO to HE110 to diagnose present fault. - Disconnect PCM.
- Key ON.
- Measure voltage between EGRVR and PWR GND circuits at the PCM harness connector.
- Voltage must read greater than 10.5V DC. For an indication of a fault, look for this voltage to drop while performing the following:
- Lightly tap on the EGR vacuum regulator solenoid.
- Wiggle the EGR vacuum regulator solenoid connector.
- Grasp the EGR vacuum regulator solenoid harness connector and wiggle wires between solenoid and PCM.
Yes No ISOLATE fault and REPAIR as necessary. Unable to duplicate or identify fault at this time. GO to Z1 .
....
uhhhhh...... lol, I asked my local Autozone about it and the guy said it might not be the EGR.. he said that the EGR normally is triggered by something.. Temp sensor etc.. he said i have a 1 in 10 shot of getting it right... great.....
uhhhhh...... lol, I asked my local Autozone about it and the guy said it might not be the EGR.. he said that the EGR normally is triggered by something.. Temp sensor etc.. he said i have a 1 in 10 shot of getting it right... great.....
its not that hard to find problem with fords pin test.....the code number will send you to what test to start from thats why i asked for code number/numbers
Did you replace the DPFE? It controls the balance between the egr and exhaust . There are two rubber hoses that connect to the driver's side exhaust and connect to the DPFE.
If your DPFE is aluminum, it needs to be replaced by the newer style which is black plastic. Around $20.
Could be the problem, but we still the the codes, not the troubleshooting chart.
If your DPFE is aluminum, it needs to be replaced by the newer style which is black plastic. Around $20.
Could be the problem, but we still the the codes, not the troubleshooting chart.
yeah i replaced everything.. The Valve, The DPFE and the EGR Selonoid.. They code is P0401
That code usually comes up when the egr actuator vacuum line leans against the egr tube and melts. It can melt through or just seal itself shut. While idling there should be vacuum on that line.
Be sure to clear the codes after any repair or change.
Be sure to clear the codes after any repair or change.
Which one is it? The boost act has 2 the pink vaccum and the Black one coming from the AIR intake.
2003 PCED OBD
SECTION 1: Description and Operation
Procedure revision date: 08/28/2003
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) System Monitor—Differential Pressure Feedback EGR
The Differential Pressure Feedback EGR System Monitor is an on-board strategy designed to test the integrity and flow characteristics of the EGR system. The monitor is activated during EGR system operation and after certain base engine conditions are satisfied. Input from the ECT, CHT, IAT, TP and CKP sensors is required to activate the monitor. Once activated, the EGR System Monitor will perform each of the tests described below during the engine modes and conditions indicated. Some of the EGR System Monitor tests are also performed during on demand self-test.
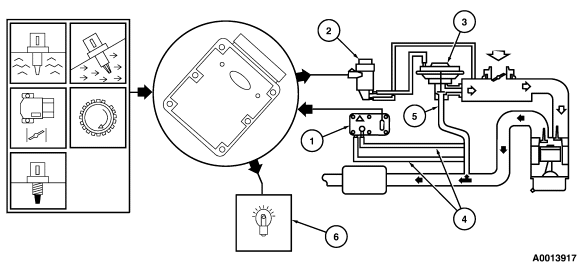
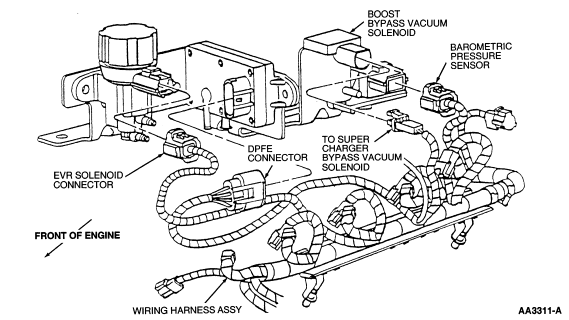
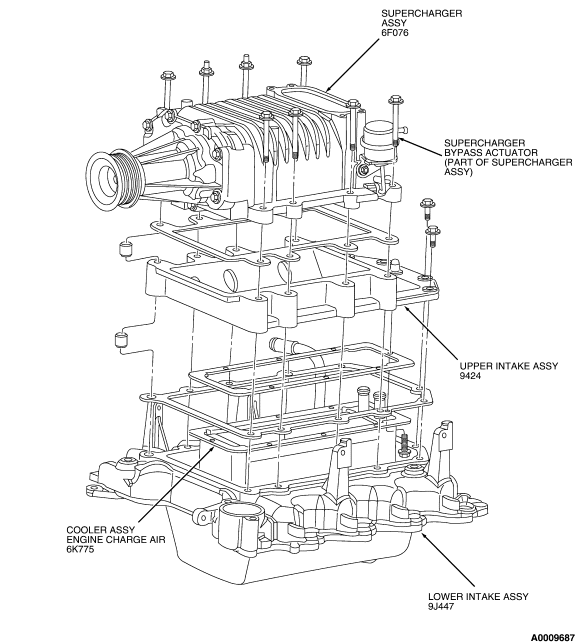
your code in the code chart says to start with pin test HE70
SECTION 1: Description and Operation
Procedure revision date: 08/28/2003
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) System Monitor—Differential Pressure Feedback EGR
The Differential Pressure Feedback EGR System Monitor is an on-board strategy designed to test the integrity and flow characteristics of the EGR system. The monitor is activated during EGR system operation and after certain base engine conditions are satisfied. Input from the ECT, CHT, IAT, TP and CKP sensors is required to activate the monitor. Once activated, the EGR System Monitor will perform each of the tests described below during the engine modes and conditions indicated. Some of the EGR System Monitor tests are also performed during on demand self-test.
- The differential pressure feedback EGR sensor and circuit are continuously tested for opens and shorts. The monitor looks for the Differential Pressure Feedback EGR circuit voltage to exceed the maximum or minimum allowable limits.
The DTCs associated with this test are DTCs P0405 and P0406.
- The EGR vacuum regulator solenoid is continuously tested for opens and shorts. The monitor looks for an EGR Vacuum Regulator circuit voltage that is inconsistent with the EGR Vacuum Regulator circuit commanded output state.
The DTC associated with this test is DTC P0403.
- The test for a stuck open EGR valve or EGR flow at idle is continuously performed whenever at idle (TP sensor indicating closed throttle). The monitor compares the Differential Pressure Feedback EGR circuit voltage at idle to the Differential Pressure Feedback EGR circuit voltage stored during key on engine off to determine if EGR flow is present at idle.
The DTC associated with this test is DTC P0402.
- The differential pressure feedback EGR sensor hoses are tested once per drive cycle for disconnect and plugging. The test is performed with EGR valve closed and during a period of acceleration. The PCM will momentarily command the EGR valve closed. The monitor looks for the differential pressure feedback EGR sensor voltage to be inconsistent for a no flow voltage. A voltage increase or decrease during acceleration while the EGR valve is closed may indicate a fault with a signal hose during this test.
The DTCs associated with this test are DTC P1405.
- The EGR flow rate test is performed during a steady state when engine speed and load are moderate and EGR vacuum regulator duty cycle is high. The monitor compares the actual Differential Pressure Feedback EGR circuit voltage to a desired EGR flow voltage for that state to determine if EGR flow rate is acceptable or insufficient. This is a system test and may trigger a DTC for any fault causing the EGR system to fail.
The DTC associated with this test is DTC P0401. DTC P1408 is similar to P0401 but performed during KOER Self-Test conditions.
- The MIL is activated after one of the above tests fails on two consecutive drive cycles.

Figure 8: EGR System Monitor - Differential Pressure Feedback EGR
your code in the code chart says to start with pin test HE70
Last edited:
being this post started with a vacuum line problem,you changed all parts already,and only code is 401,pin test HE91 looks like where i would start..
keep us updated on this
keep us updated on this
So i got two new hoses and connected them to the EGR sensor and the exhaust pipe, and drove around all day. Nothing so far but i will keep you updated if the light comes back on
Users who are viewing this thread
Total: 2 (members: 0, guests: 2)


